“the Impact Of Student Loans On Parents And Grandparents” – The amount of student debt in America is the size of the economy of Brazil or Australia. According to the US government, more than 45 million people have a total debt of $1.6 trillion.
As the cost of higher education has continued to rise over the past half century, this figure has increased dramatically. The increase in spending was significantly higher than the increase in spending by many other households.
“the Impact Of Student Loans On Parents And Grandparents”

The rising cost of college comes at a time when students are receiving less support from the state and students and families are burdened with more loans to finance their education.
Who Is Impacted By Student Loan Forgiveness And How?
According to an analysis by the Urban Institute, about 60 percent of higher education spending before the pandemic fell from 70 percent in the 1970s, and funding from states in particular has steadily declined.
The share of state and local government spending on higher education is declining Share of higher education spending
To address the growing crisis, President Biden on Wednesday announced a plan to eliminate massive amounts of student debt for millions of people. It was a step toward what Mr. Biden said was a campaign promise to alleviate an unsustainable problem that has plagued Americans for generations.
“The burden is so heavy that even if you graduate,” he said, “you may not have access to the middle-class life that a college degree once offered.”
Canceling Student Loan Debt Is Poor Economic Stimulus
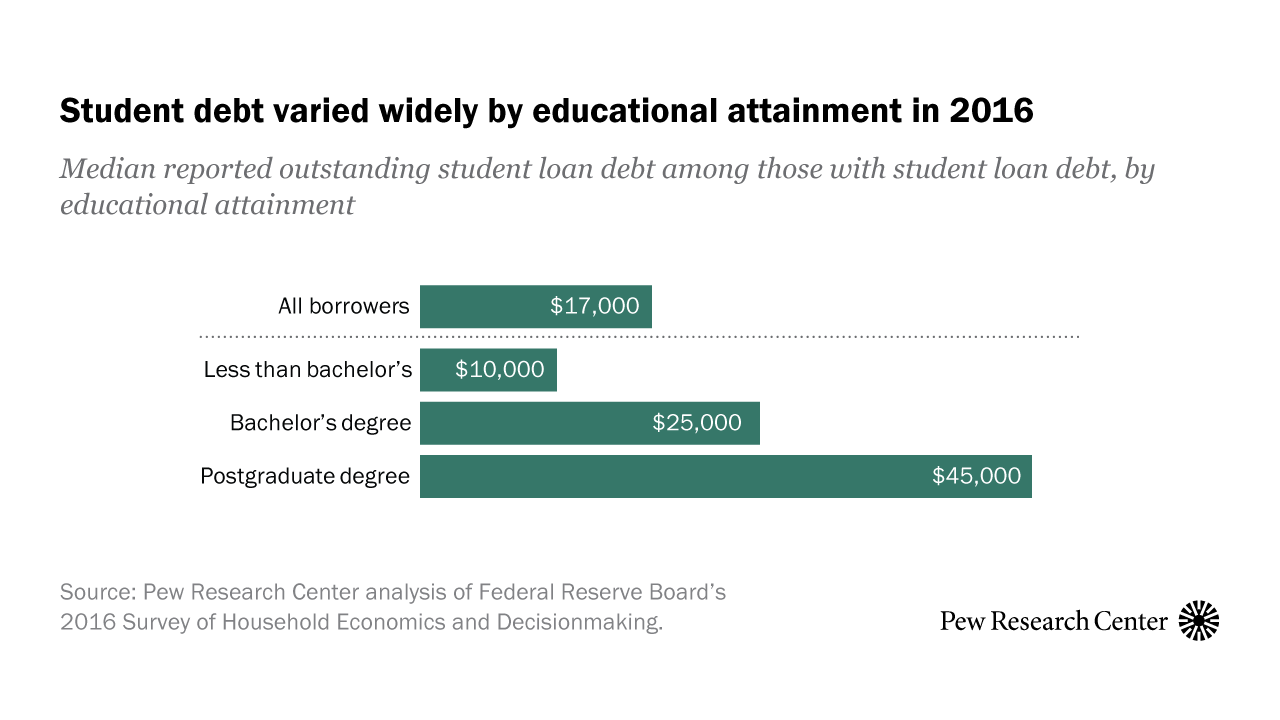
A Department of Education analysis shows that an undergraduate student with loans graduates with about $25,000 in debt.
Under the plan, borrowers would be eligible for $10,000 in debt relief if they earn less than $125,000 a year or are in households earning less than $250,000. 2021 or 2020.)
Blacks take on more student debt… Share of families with education loans by race

Source: Federal Reserve Notes: Black and white groups do not include people who identify as Hispanic. The data comes from the Federal Reserve’s triennial survey of consumer finances.
Communities Of Color In Crisis: Examining Racial Disparities In Student Loan Debt And Borrower Outcomes
… Total Student Loan Balances by Age, with Millennials Debt More Than Older and Younger Generations
As the pandemic brought the global economy to a standstill in 2020, President Trump announced a moratorium on student loan repayments and forced interest rates to drop to zero. Mr. Biden has adopted a similar policy. These actions have helped millions of people reduce their credit balances and prevent borrowers from defaulting on their loans.
Still, since the pandemic began, the number of people whose credit balances have remained unchanged or increased has risen sharply.
Pandemic moratorium reduces defaults, but balances still remain Borrowers by credit status at year-end
Debt And No Degree’: Biden Cancels $20k In Student Loan Debt: Recap
On Wednesday, Mr. Biden announced that the pause in payments during the pandemic will end at the end of the year. He also reiterated his commitment to helping low- and middle-income households in particular. How to do this has been a topic of debate both inside and outside the White House.
One clause of the program includes an income limit: Debt relief can only be applied to individuals or families with incomes below a certain amount. The goal of the rule, the White House said, is to make sure no one with high incomes gets the benefit.
An independent analysis by the Wharton School of Business found that households earning between $51,000 and $82,000 a year would see the most relief, regardless of whether the income cap applies. That’s in part because more people in the middle income bracket have student loans.

Source: Wharton Budget Model Household Income Quintiles from 2022. This analysis considers additional benefits for Pell Grant recipients.
Does The Stress Of Student Loan Debt Negatively Impact Heart Health?
Millions of people will benefit from the relief, but Mr. Biden’s announcement has sparked heated debate about its merits.
Analysts and officials on both sides of the political aisle worry about the plan’s impact on inflation, partly because debt relief could inject money into the economy. (White House economic advisers have argued that the plan, which includes debt restructuring and income restraints, would have a negligible impact on consumer price growth.)
Others argue that while the relief may help many people, it doesn’t address the underlying problems of how expensive college is. Some economists have even warned that the move could encourage colleges and universities to raise prices under the federal government bill.
“I understand that not everything I’m announcing today is going to please everyone,” Mr. Biden said on Wednesday. “But I believe my plan is responsible and fair.”Note: We published a follow-up article on June 3, 2021, calculating the fiscal multipliers for eliminating $10,000 and $50,000 in federal student loan debt, which you can find here possible . We calculate a multiplier of .02x to .27x with a central calculation of .13x for a $10,000 debt cancellation and .10x for a $50,000 cancellation.
How The Supreme Court’s Decision May Affect Student Loan Borrowers
Faced with a weak economy still reeling from the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, there have been a number of calls for President-elect Joe Biden to support the economic recovery by canceling some or all of his student loan debt.
Whether or not the president has the power to cancel the debt by executive order is a matter of debate as to whether it is generally good policy. However, one thing is clear: Student loan cancellation is an ineffective form of stimulus and provides little near-term economic boost relative to spending. Assuming the loans are forgiven tax-free, we estimate an economic multiplier of 0.08x to 0.23x.
There are a number of benefits and costs associated with canceling student loans. But as a stimulus measure, its “monetary benefit” is far less than many of the alternatives being considered or the COVID relief already in place.

Economic stimulus works by increasing aggregate spending when the economy is in a period of weakness. Still, student loan debt forgiveness has a small impact on what can be spent.
How Women Are Affected By Student Loans
Total loan forgiveness would increase household wealth by about $1.5 trillion (at the same cost to the government), but that’s not the same as sending households $1.5 trillion in cash. Instead of costing the average household $15,000 or $20,000, it frees up their monthly interest and principal payments, which typically cost the borrower $200 to $300 per month.
In other words, because borrowers often pay off their loans over 10, 15, or even 30 years, debt cancellation increases their available cash for only a portion of total debt forgiveness.
Our analysis of the student aid portfolio shows that eliminating $1.5 trillion in loans would cost $90 billion or less in 2021 and $450 billion or less over 5 years.
Just canceling some debt—say, by putting down $10,000 or $50,000—reduces the cost and cash flow impact roughly proportionally.
Watch: How Student Loan Debt Disproportionately Hurts Black Borrowers
These numbers may overestimate new cash flow given current tax laws. Generally, the debt forgiveness amount is treated as income and is taxable. As Jason Furman, former chairman of President Obama’s Council of Economic Advisers, noted, the immediate taxes paid for this forgiveness could be greater than the savings for near-term loan payments. According to this tax regime (some may change it or it is a misunderstanding of the current law) the debt can be forgiven
On the other hand, the absence of future debt can lead some individuals and households to spend more by drawing from their savings or by taking alternative loans, a phenomenon known as the wealth effect. Empirical evidence shows that an increase in the value of a home or stock portfolio increases costs by 3 to 6 cents for every dollar of increase in wealth. That translates into about $50 to $100 billion in additional costs. That’s a small economic impact compared to the $1.5 trillion cost.
Not only does loan cancellation give households relatively little spendable cash, but the cash it offers is poorly targeted in terms of incentives.
Stimulus dollars spent instead of austerity will provide a strong boost to economic output in the near future. In general, those with low incomes or those who have recently experienced negative income shocks are more likely to expend additional resources. Still, most of the debt relief will go to high-income earners and those who have maintained their incomes during the current crisis.
Impact Of Student Loans On Black Graduates
Many of those hardest hit by the current economic crisis have little or no student debt. More than 70 percent of current unemployed workers do not have a bachelor’s degree, including 43 percent who have not attended college at all. Meanwhile, less than one-third of all student debt is held by households without a bachelor’s degree and less than one-tenth by those without a college degree. In fact, two-fifths of all student debt is held by households
Parents paying student loans, student loans without parents, student loans parents, student loans divorced parents, parents plus student loans, parents and student loans, are student loans based on parents income, student loans based on parents income, student loans for parents, parents pay student loans, parents income and student loans, student loans parents income